Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems . Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. the monocot cambium is a lateral meristem responsible for secondary growth in some monocotyledons of. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. Apical meristems give rise to. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant:
from www.numerade.com
Apical meristems give rise to. meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant: meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. the monocot cambium is a lateral meristem responsible for secondary growth in some monocotyledons of. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ].
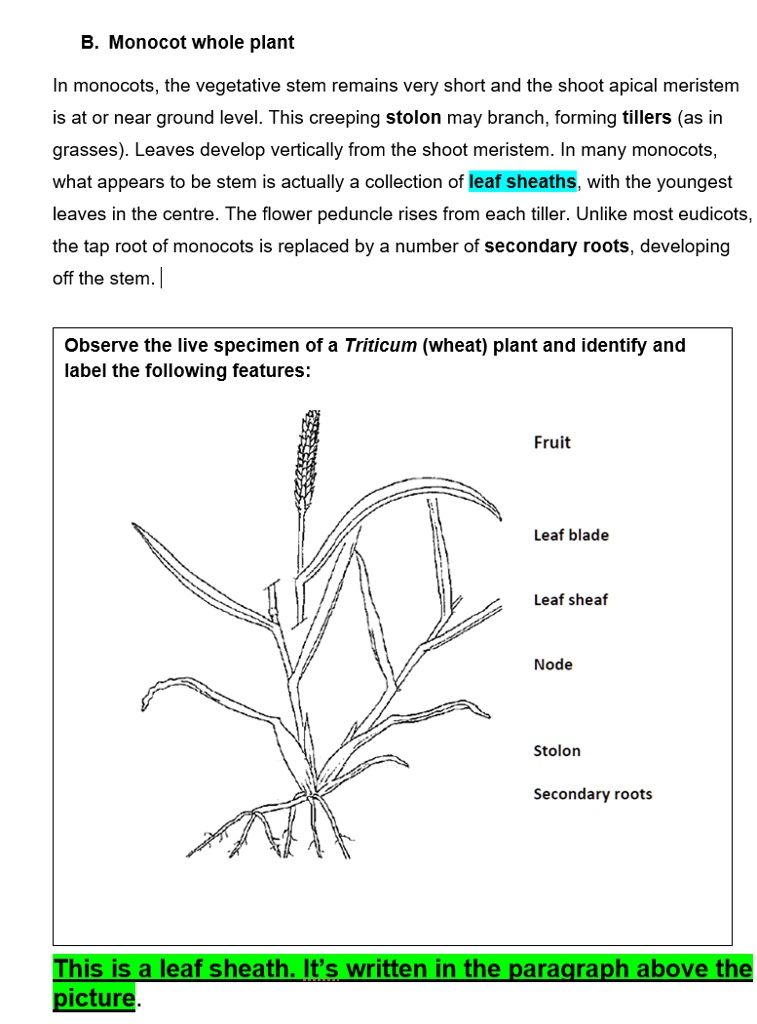
SOLVED Monocot whole plant In monocots, the vegetative stem remains
Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. the monocot cambium is a lateral meristem responsible for secondary growth in some monocotyledons of. meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant: however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. Apical meristems give rise to. Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ].
From propg.ifas.ufl.edu
Cell Types, Meristems Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.pinterest.cl
Plant science, Biology, Botany Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant: however, in monocots. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.brainkart.com
Apical meristems Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant: however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. Apical meristems give rise to. meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Root Apical Meristem And Shoot Apical Meristem Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. the monocot cambium is a lateral meristem responsible for secondary growth in some monocotyledons of. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. Apical meristems give. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT PLANTS PowerPoint Presentation ID2055706 Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems Apical meristems give rise to. however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Apical Meristem Cross Section Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. Apical meristems give rise to. Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. apical meristem, region of cells capable of. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Monocot whole plant In monocots, the vegetative stem remains Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From design.udlvirtual.edu.pe
What Is Apical Meristem Design Talk Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant: however, in monocots. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From mmegias.webs.uvigo.es
Plant tissues. Meristems. Root apical meristem. Atlas of plant and Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. Apical meristems give rise to. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems,. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 3 Introduction to plant structure PowerPoint Presentation Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems the monocot cambium is a lateral meristem responsible for secondary growth in some monocotyledons of. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. in. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Ch. 31 Plant Structure, Growth and Differentiation PowerPoint Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From slideplayer.com
Tissues Chapter ppt download Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between.. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.pw.live
Meristems Based On Origin Types of Meristems Based On Origin Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant: meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.linstitute.net
IB DP Biology HL复习笔记9.3.1 Plant Growth翰林国际教育 Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. Apical meristems give rise to. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. the monocot cambium is a lateral meristem. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From education-portal.com
Plant Meristem Definition & Function Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. meristematic tissues consist of three types, based on their location in the plant: however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. Web. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Plant Structure and Growth PowerPoint Presentation, free download Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the base of a single cotyledon [ 1 ]. Apical meristems give rise to. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Monocots And Dicots Seeds Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork. Apical meristems give rise to. Apical meristems contain meristematic tissue. apical meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in the root and shoot tips in plants. in monocots, such as rice and. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 1 from Flower development in rice. Semantic Scholar Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems Apical meristems give rise to. however, in monocots apical meristems are located only on the root tips, which are at a basal location near the soil. monocot stems do not have lateral meristems, but often have intercalary meristems inserted in the stems between. in monocots, such as rice and maize, the sam is formed laterally, at the. Do Monocots Have Apical Meristems.